Difference between revisions of "v0.13:Symbols"
m (→Finding Symbols) |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Finding Symbols == | == Finding Symbols == | ||
| − | Symbols can be discovered a couple ways. The first and most basic way is finding a village containing a [[Archivist]]; The [[Archivist]]'s house will also contain a couple pages. The second and most common way to find Symbols would be to explore an age. Ages will have randomly spawning temples made of cobblestone that will contain several pages and possibly some [[Sealed Notebook]]s. The third and final way would be to explore dungeons. Dungeons have a chance to contain symbols and sealed notebooks. | + | Symbols can be discovered a couple ways. The first and most basic way is finding a village containing a [[Archivist]]; The [[Archivist]]'s house will also contain a couple pages. The second and most common way to find Symbols would be to explore an age. Ages will have randomly spawning temples made of cobblestone that will contain several pages and possibly some [[Sealed Notebook]]s. The third and final way would be to explore dungeons. Dungeons have a chance to contain symbols and sealed notebooks.(Verify) |
=Pages= | =Pages= | ||
Revision as of 18:16, 28 July 2018
v0.13 · Older This article is about the current version of Mystcraft. |
Symbols are key to creating Ages with a Descriptive Book in Mystcraft. Symbol define aspects of the Age created, allowing for customization and eliminating randomly decided aspects of the book's Age.
See Writing for how to use these symbols effectively.
Contents
Finding Symbols
Symbols can be discovered a couple ways. The first and most basic way is finding a village containing a Archivist; The Archivist's house will also contain a couple pages. The second and most common way to find Symbols would be to explore an age. Ages will have randomly spawning temples made of cobblestone that will contain several pages and possibly some Sealed Notebooks. The third and final way would be to explore dungeons. Dungeons have a chance to contain symbols and sealed notebooks.(Verify)
Pages
Symbols come on sheets of paper, called pages. As of 0.12.3.00 pages do not vary in quality or condition. Symbols can be written to paper or pages using a Writing Desk.
Kinds of Symbols
Biome Distributions
Celestials
Effects
Lighting
Visuals
Weather
World Feature
World Landscape
Modifiers
Modifiers allow for customizing other symbols by specifying things like colors or block types.
Modifiers are written before the symbol they modify, for instance Cyan Color ➡ Sky Color.
Angle Modifiers
Angle Modifiers are used for Celestial positioning. They define where on the horizon the celestial will rise.
Angles will consume other Angles and produce a point halfway between the two. North followed by West will produce a northwest angle. When more than two angles are blended, a rolling average will be used such as ((W + X) + Y) + Z.
In cases where there are two possible averages, the average will be clockwise from the first angle. For example, North ➡ South will result in East, while South ➡ North will result in West.
| Symbol | Name | Angle |
|---|---|---|
|
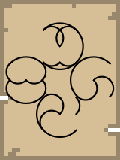
North Direction | 0/360 |
|
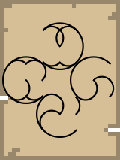
East Direction | 90 |
|
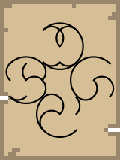
South Direction | 180 |
|
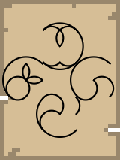
West Direction | 270 |
Biome Modifiers
Block Modifiers
Color Modifiers
Gradients
Length Modifiers
Length Modifiers are used for Celestial movement, as well as Gradients. They define how quickly the celestial will orbit or how quickly colors will last. Lower values are faster, higher values are slower. Note that daytime is ½ of an orbit.
Lengths will consume other Lengths and produce a point halfway between the two. When more than two Lengths are blended, a rolling average will be used such as ((W + X) + Y) + Z.
Phase Modifiers
Phase Modifiers are used for Celestial positioning. They define where in the sky the celestial will start. This is especially relevant for celestials with fixed positions, but can also be used to have multiple celestials that rise at different times of the day.
Phases will consume other Phases and produce a point halfway between the two. When more than two Phases are blended, a rolling average will be used such as ((W + X) + Y) + Z.
In cases where there are two possible averages, the average will be forward in the cycle from the first angle. For example, Rising ➡ Setting will result in Zenith, while Setting ➡ Rising will result in Nadir.